Difference between revisions of "GlyA"
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
* '''Operon:''' ''[[glyA]]'' | * '''Operon:''' ''[[glyA]]'' | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
Revision as of 09:10, 8 April 2009
- Description: serine hydroxymethyltransferase
| Gene name | glyA |
| Synonyms | glyC, ipc-34d |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | serine hydroxymethyltransferase |
| Function | biosynthesis of glycine |
| MW, pI | 45 kDa, 5.475 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1245 bp, 415 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | upp, ywlG |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 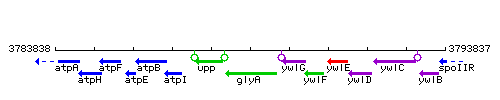
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: glyA
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Eymann et al. (2007) Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis. Proteomics 7: 3509-3526. PubMed
- Lévine et al. (2006) Analysis of the dynamic Bacillus subtilis Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphoproteome implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes. Proteomics 6: 2157-2173 PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed