Difference between revisions of "GlpK"
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 151 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 151 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 6111 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 6111 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 263 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 571 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1140 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 17 April 2014
- Description: glycerol kinase
| Gene name | glpK |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glycerol kinase |
| Function | glycerol utilization |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: glpK | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GlpK | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: glpK | |
| MW, pI | 54 kDa, 4.985 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1488 bp, 496 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glpF, glpD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 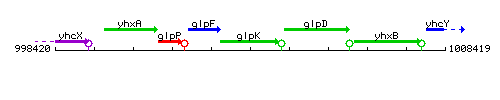
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed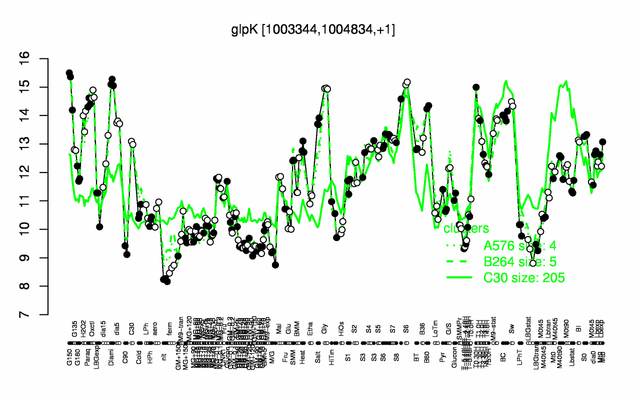
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, CcpA regulon, GlpP regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU09290
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU09290
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + glycerol = ADP + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FGGY kinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU09290
- UniProt: P18157
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.30
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 151 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 6111 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 263 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 571 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1140 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Josef Deutscher, Paris-Grignon, France
Your additional remarks
References
Onuma Chumsakul, Hiroki Takahashi, Taku Oshima, Takahiro Hishimoto, Shigehiko Kanaya, Naotake Ogasawara, Shu Ishikawa
Genome-wide binding profiles of the Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB and its homolog Abh reveals their interactive role in transcriptional regulation.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(2);414-28
[PubMed:20817675]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joanne I Yeh, Regina Kettering, Ruth Saxl, Alexa Bourand, Emmanuelle Darbon, Nathalie Joly, Pierre Briozzo, Josef Deutscher
Structural characterizations of glycerol kinase: unraveling phosphorylation-induced long-range activation.
Biochemistry: 2009, 48(2);346-56
[PubMed:19102629]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Emmanuelle Darbon, Pascale Servant, Sandrine Poncet, Josef Deutscher
Antitermination by GlpP, catabolite repression via CcpA and inducer exclusion triggered by P-GlpK dephosphorylation control Bacillus subtilis glpFK expression.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 43(4);1039-52
[PubMed:11929549]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V Charrier, E Buckley, D Parsonage, A Galinier, E Darbon, M Jaquinod, E Forest, J Deutscher, A Claiborne
Cloning and sequencing of two enterococcal glpK genes and regulation of the encoded glycerol kinases by phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent, phosphotransferase system-catalyzed phosphorylation of a single histidyl residue.
J Biol Chem: 1997, 272(22);14166-74
[PubMed:9162046]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christina Wehtje, Lena Beijer, Rune-Pär Nilsson, Blanka Rutberg
Mutations in the glycerol kinase gene restore the ability of a ptsGHI mutant of Bacillus subtilis to grow on glycerol.
Microbiology (Reading): 1995, 141 ( Pt 5);1193-1198
[PubMed:7773413]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Beijer, L Rutberg
Utilisation of glycerol and glycerol 3-phosphate is differently affected by the phosphotransferase system in Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1992, 100(1-3);217-20
[PubMed:1335945]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)