Difference between revisions of "GlnA"
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 8140 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 8140 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 11334 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 11334 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 16645 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 11115 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 11598 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' GP247 (''glnA::cat''), available in [[Stülke]] lab | * '''Mutant:''' GP247 (''glnA::cat''), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 17 April 2014
- Description: trigger enzyme: glutamine synthetase and effector of TnrA and GlnR
| Gene name | glnA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: glutamine synthetase |
| Function | glutamine biosynthesis, control of TnrA and GlnR activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: glnA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GlnA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: glnA | |
| MW, pI | 50 kDa, 4.874 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1332 bp, 444 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glnR, ynxB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 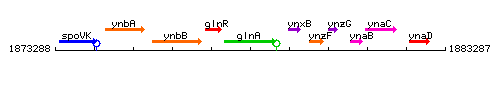
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, transcription factors and their control, trigger enzyme, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU17460
Phenotypes of a mutant
auxotrophic for glutamine
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU17460
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + L-glutamate + NH3 = ADP + phosphate + L-glutamine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: glutamine synthetase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: K(M) for: Glu: 27 mM, ATP: 2.4 mM, ammonium: 0.18 mM; v(max): 3.7 µmol/min/mg
- Domains: glutamate binding flap (aa 300 ... 306: protects unstable intermediates from abberant hydrolysis)
- Modification:
- Cofactors: Mg(2+)
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU17460
- Structure:
- 4LNN (apo-GS) PubMed
- 3QAJ (complex with ATP)
- A general discussion of GS structure
- UniProt: P12425
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.3.1.2
Additional information
GlnA is a homooligomer of 12 subunits
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 8140 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 11334 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 16645 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 11115 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 11598 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP247 (glnA::cat), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- expression/ purification from E. coli, with N-terminal Strep-tag (in pGP172): pGP174, available in Stülke lab
- pGP177 (N-terminal Strep-tag, purification from B. subtilis, for SPINE, in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in Karl Forchhammer lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Susan Fisher, Boston, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
David S Murray, Nagababu Chinnam, Nam Ky Tonthat, Travis Whitfill, Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher, Maria A Schumacher
Structures of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase dodecamer reveal large intersubunit catalytic conformational changes linked to a unique feedback inhibition mechanism.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(50);35801-11
[PubMed:24158439]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ksenia Fedorova, Airat Kayumov, Kathrin Woyda, Olga Ilinskaja, Karl Forchhammer
Transcription factor TnrA inhibits the biosynthetic activity of glutamine synthetase in Bacillus subtilis.
FEBS Lett: 2013, 587(9);1293-8
[PubMed:23535029]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Airat Kayumov, Annette Heinrich, Kseniya Fedorova, Olga Ilinskaya, Karl Forchhammer
Interaction of the general transcription factor TnrA with the PII-like protein GlnK and glutamine synthetase in Bacillus subtilis.
FEBS J: 2011, 278(10);1779-89
[PubMed:21435182]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher
Functional roles of the conserved Glu304 loop of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(19);5018-25
[PubMed:20656908]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Nico Pietack, Dörte Becher, Sebastian R Schmidl, Milton H Saier, Michael Hecker, Fabian M Commichau, Jörg Stülke
In vitro phosphorylation of key metabolic enzymes from Bacillus subtilis: PrkC phosphorylates enzymes from different branches of basic metabolism.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2010, 18(3);129-40
[PubMed:20389117]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Susan H Fisher, Lewis V Wray
Novel trans-Acting Bacillus subtilis glnA mutations that derepress glnRA expression.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(8);2485-92
[PubMed:19233925]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher
Bacillus subtilis GlnR contains an autoinhibitory C-terminal domain required for the interaction with glutamine synthetase.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 68(2);277-85
[PubMed:18331450]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Susan H Fisher, Lewis V Wray
Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase regulates its own synthesis by acting as a chaperone to stabilize GlnR-DNA complexes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2008, 105(3);1014-9
[PubMed:18195355]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Susan H Fisher, Lewis V Wray
Feedback-resistant mutations in Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase are clustered in the active site.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(16);5966-74
[PubMed:16885465]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jill M Zalieckas, Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher
Cross-regulation of the Bacillus subtilis glnRA and tnrA genes provides evidence for DNA binding site discrimination by GlnR and TnrA.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(7);2578-85
[PubMed:16547045]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Alain Lévine, Françoise Vannier, Cédric Absalon, Lauriane Kuhn, Peter Jackson, Elaine Scrivener, Valérie Labas, Joëlle Vinh, Patrick Courtney, Jérôme Garin, Simone J Séror
Analysis of the dynamic Bacillus subtilis Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphoproteome implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2157-73
[PubMed:16493705]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher
A feedback-resistant mutant of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase with pleiotropic defects in nitrogen-regulated gene expression.
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(39);33298-304
[PubMed:16055443]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Susan H Fisher, Jaclyn L Brandenburg, Lewis V Wray
Mutations in Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase that block its interaction with transcription factor TnrA.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(3);627-35
[PubMed:12139611]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L V Wray, J M Zalieckas, S H Fisher
Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase controls gene expression through a protein-protein interaction with transcription factor TnrA.
Cell: 2001, 107(4);427-35
[PubMed:11719184]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L V Wray, A E Ferson, K Rohrer, S H Fisher
TnrA, a transcription factor required for global nitrogen regulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1996, 93(17);8841-5
[PubMed:8799114]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S W Brown, A L Sonenshein
Autogenous regulation of the Bacillus subtilis glnRA operon.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(8);2450-4
[PubMed:8636055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H J Schreier, C A Rostkowski, E M Kellner
Altered regulation of the glnRA operon in a Bacillus subtilis mutant that produces methionine sulfoximine-tolerant glutamine synthetase.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(3);892-7
[PubMed:8093698]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H J Schreier, S W Brown, K D Hirschi, J F Nomellini, A L Sonenshein
Regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene expression by the product of the glnR gene.
J Mol Biol: 1989, 210(1);51-63
[PubMed:2573733]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M A Strauch, A I Aronson, S W Brown, H J Schreier, A L Sonenhein
Sequence of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene region.
Gene: 1988, 71(2);257-65
[PubMed:2906311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S H Fisher, A L Sonenshein
Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase mutants pleiotropically altered in glucose catabolite repression.
J Bacteriol: 1984, 157(2);612-21
[PubMed:6141156]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)