Difference between revisions of "CodY"
(→Biological materials) |
(→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
| − | ** GP566, available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** GP566, available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
** a ''[[codY]]::erm'' mutant is available in [[Linc Sonenshein]]'s lab | ** a ''[[codY]]::erm'' mutant is available in [[Linc Sonenshein]]'s lab | ||
** a ''[[codY]]::spc'' (BB1043) mutant is available in [[Linc Sonenshein]]'s, [[Fabian Commichau]]'s and [[Jörg Stülke]]'s labs | ** a ''[[codY]]::spc'' (BB1043) mutant is available in [[Linc Sonenshein]]'s, [[Fabian Commichau]]'s and [[Jörg Stülke]]'s labs | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 19 June 2014
- Description: regulation of a large regulon (more than 100 genes and operons) in response to branched-chain amino acid limitation
| Gene name | codY |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional pleiotropic repressor |
| Function | regulation of a large regulon in response to
branched-chain amino acid limitation to the presence of branched-chain amino acids |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: codY | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CodY | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: codY | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 4.75 |
| Gene length, protein length | 777 bp, 259 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | clpY, flgB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 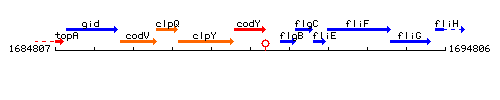
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed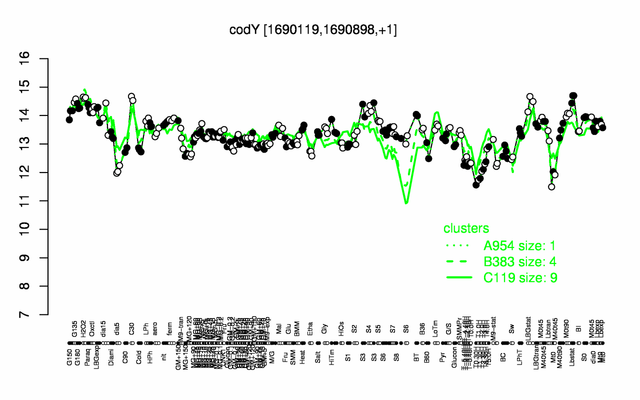
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CodY regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16170
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
- the mutation suppresses the mucoid phenotype of motA or motB mutants due to loss of DegU phosphorylation and concomitant reduced expression of the capB-capC-capA-capE operon PubMed
- inactivation of codY suppresses the requirement of a relA sasA sasB triple mutant for branched chain amino acids, methionine and threonine PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16170
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: codY family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes/ operons controlled by CodY
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: contains a GAF domain (ligand binding domain)
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-215 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity: GTP and branched chained amino acids (BCAA) increase the affinity of CodY for its DNA target sequences PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16170
- UniProt: P39779
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
- the intracellular concentration of CodY is about 2.5 myM (according to PubMed)
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 955 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 3409 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 350 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 351 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 272 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP566, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- a codY::erm mutant is available in Linc Sonenshein's lab
- a codY::spc (BB1043) mutant is available in Linc Sonenshein's, Fabian Commichau's and Jörg Stülke's labs
- Expression vector:
- for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP245, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
- Tony Wilkinson, York University, U.K. homepage
- Oscar Kuipers, University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Tobias Geiger, Christiane Wolz
Intersection of the stringent response and the CodY regulon in low GC Gram-positive bacteria.
Int J Med Microbiol: 2014, 304(2);150-5
[PubMed:24462007]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sabine Brantl, Andreas Licht
Characterisation of Bacillus subtilis transcriptional regulators involved in metabolic processes.
Curr Protein Pept Sci: 2010, 11(4);274-91
[PubMed:20408793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Abraham L Sonenshein
Control of key metabolic intersections in Bacillus subtilis.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2007, 5(12);917-27
[PubMed:17982469]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Abraham L Sonenshein
CodY, a global regulator of stationary phase and virulence in Gram-positive bacteria.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2005, 8(2);203-7
[PubMed:15802253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
The CodY regulon
Shaun R Brinsmade, Elizabeth L Alexander, Jonathan Livny, Arion I Stettner, Daniel Segrè, Kyu Y Rhee, Abraham L Sonenshein
Hierarchical expression of genes controlled by the Bacillus subtilis global regulatory protein CodY.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2014, 111(22);8227-32
[PubMed:24843172]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genome-wide identification of Bacillus subtilis CodY-binding sites at single-nucleotide resolution.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2013, 110(17);7026-31
[PubMed:23569278]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of CodY-binding sites in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(4);1224-36
[PubMed:18083814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications