BglP
- Description: write here
| Gene name | bglP |
| Synonyms | sytA |
| Essential | |
| Product | phosphotransferase system (PTS) beta-glucoside-specific enzyme IIBCA component (EC 2.7.1.69) |
| Function | |
| MW, pI | 64 kDa, 6.809 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1827 bp, 609 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 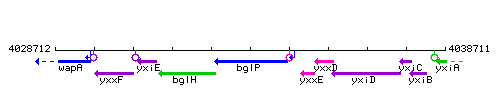
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry:
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation: induced by salicin PubMed, repressed by glucose (catabolite repression)
- Regulatory mechanism: Induction: LicT-dependent RNA switch (antitermination), catabolite repression: repression by CcpA (CcpA binding site overlaps -35 region) and lack of LicT-dependent antitermination in the presence of gucose due to the requirement of LicT to be phosphorylated by HPr
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Le Coq, D., Lindner, C., Krüger, S., Steinmetz, M. & Stülke, J. (1995) New ß-glucosides (bgl) genes in Bacillus subtilis: The bglP gene product has both transport and regulatory functions, similar to that of the Escherichia coli BglF protein. J. Bacteriol. 177: 1527-1535. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed