AcsA
- Description: acetyl-CoA synthetase
| Gene name | acsA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetyl-CoA synthetase) |
| Function | utilization of acetate, fatty acids |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: acsA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: acsA | |
| MW, pI | 64 kDa, 5.547 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1716 bp, 572 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ytzK, acuA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 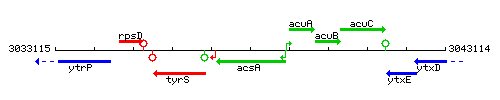
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed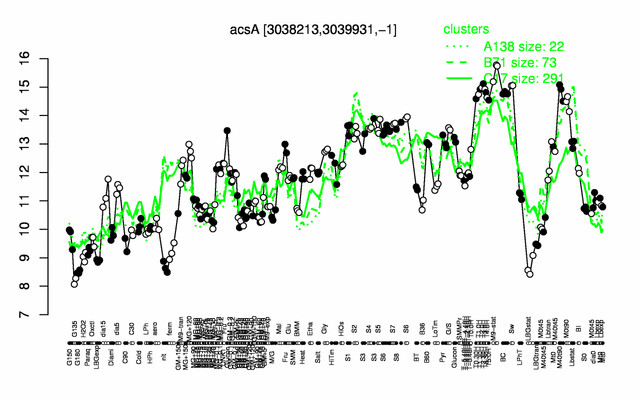
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, utilization of lipids
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29680
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29680
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + acetate + CoA = AMP + diphosphate + acetyl-CoA (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: acetylated on Lys-549 by AcuA, this results in inactivation PubMed, deacetylated by SrtN and AcuC deacetylates (and thereby activates) AcsA PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29680
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39062
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.2.1.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1037 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1384 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3490 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP1212 (acsA::kan), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Eric L Hegg
Unraveling the structure and mechanism of acetyl-coenzyme A synthase.
Acc Chem Res: 2004, 37(10);775-83
[PubMed:15491124]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V J Starai, J C Escalante-Semerena
Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase (AMP forming).
Cell Mol Life Sci: 2004, 61(16);2020-30
[PubMed:15316652]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Paul A Lindahl
Acetyl-coenzyme A synthase: the case for a Ni(p)(0)-based mechanism of catalysis.
J Biol Inorg Chem: 2004, 9(5);516-24
[PubMed:15221478]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Bogumiła C Marciniak, Monika Pabijaniak, Anne de Jong, Robert Dűhring, Gerald Seidel, Wolfgang Hillen, Oscar P Kuipers
High- and low-affinity cre boxes for CcpA binding in Bacillus subtilis revealed by genome-wide analysis.
BMC Genomics: 2012, 13;401
[PubMed:22900538]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Jeffrey G Gardner, Jorge C Escalante-Semerena
In Bacillus subtilis, the sirtuin protein deacetylase, encoded by the srtN gene (formerly yhdZ), and functions encoded by the acuABC genes control the activity of acetyl coenzyme A synthetase.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(6);1749-55
[PubMed:19136592]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeffrey G Gardner, Jorge C Escalante-Semerena
Biochemical and mutational analyses of AcuA, the acetyltransferase enzyme that controls the activity of the acetyl coenzyme a synthetase (AcsA) in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(14);5132-6
[PubMed:18487328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of CodY-binding sites in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(4);1224-36
[PubMed:18083814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Uwe Linne, Antje Schäfer, Milton T Stubbs, Mohamed A Marahiel
Aminoacyl-coenzyme A synthesis catalyzed by adenylation domains.
FEBS Lett: 2007, 581(5);905-10
[PubMed:17303131]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jeffrey G Gardner, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin, Jorge C Escalante-Semerena
Control of acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase (AcsA) activity by acetylation/deacetylation without NAD(+) involvement in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(15);5460-8
[PubMed:16855235]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, A J Turinsky, T M Henkin
Catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis acetate and acetoin utilization genes by CcpA.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4527-33
[PubMed:7913927]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, D A Waters, T Y Takova, T M Henkin
Identification of genes involved in utilization of acetate and acetoin in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 10(2);259-71
[PubMed:7934817]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)