AtpG
Revision as of 13:33, 17 April 2014 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: ATP synthase, part of the F1 complex (subunit gamma)
| Gene name | atpG |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP synthase (subunit gamma)) |
| Function | ATP synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: atpG | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: AtpG | |
| MW, pI | 31 kDa, 6.642 |
| Gene length, protein length | 861 bp, 287 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | atpD, atpA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 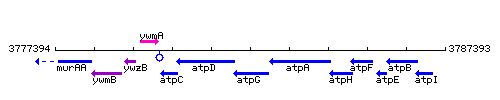
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ATP synthesis, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36820
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU36820
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP synthesis see a video
- Protein family: ATPase gamma chain family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane, peripheral via theF0 complex
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU36820
- Structure: see here an overview on ATPase structure
- UniProt: P37810
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 446 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2915 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 502 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 668 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
M Santana, M S Ionescu, A Vertes, R Longin, F Kunst, A Danchin, P Glaser
Bacillus subtilis F0F1 ATPase: DNA sequence of the atp operon and characterization of atp mutants.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(22);6802-11
[PubMed:7961438]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)