DegS
- Description: two-component sensor kinase for exoenzyme and competence regulation, kinase activity is activated in response to inhibition of flagellar rotation
| Gene name | degS |
| Synonyms | sacU |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | regulation of degradative enzyme and genetic competence |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: degS | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DegS | |
| MW, pI | 44 kDa, 5.988 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1155 bp, 385 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | degU, yvyE |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 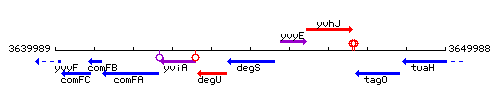
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed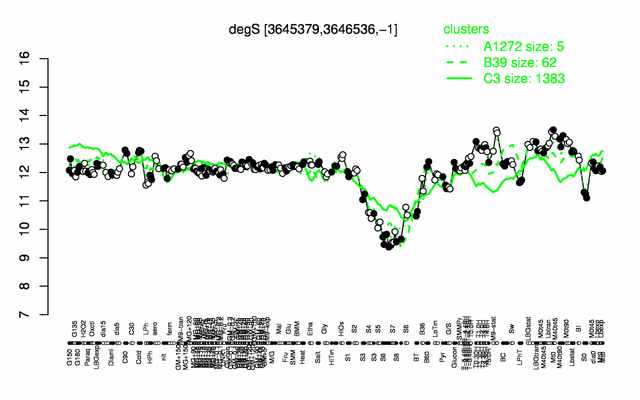
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein modification, transcription factors and their control, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35500
Phenotypes of a mutant
- the mutation suppresses the mucoid phenotype of motA or motB mutants due to loss of DegU phosphorylation and concomitant reduced expression of the capB-capC-capA-capE operon PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35500
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- aa 12 ... 170: unknown DegS domain
- aa 180 ... 248: HisKA_3 domain (autophosphorylation)
- aa 289 ... 384: HATPase_c
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: Cytoplasm (Homogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35500
- Structure:
- UniProt: P13799
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 69 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Tarek Msadek, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Jia Mun Chan, Sarah B Guttenplan, Daniel B Kearns
Defects in the flagellar motor increase synthesis of poly-γ-glutamate in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(4);740-53
[PubMed:24296669]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lynne S Cairns, Victoria L Marlow, Emma Bissett, Adam Ostrowski, Nicola R Stanley-Wall
A mechanical signal transmitted by the flagellum controls signalling in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 90(1);6-21
[PubMed:23888912]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Thi-Huyen Do, Yuki Suzuki, Naoki Abe, Jun Kaneko, Yoshifumi Itoh, Keitarou Kimura
Mutations suppressing the loss of DegQ function in Bacillus subtilis (natto) poly-γ-glutamate synthesis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(23);8249-58
[PubMed:21965392]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Carsten Jers, Ahasanul Kobir, Elsebeth Oline Søndergaard, Peter Ruhdal Jensen, Ivan Mijakovic
Bacillus subtilis two-component system sensory kinase DegS is regulated by serine phosphorylation in its input domain.
PLoS One: 2011, 6(2);e14653
[PubMed:21304896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Kazuo Kobayashi
Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(2);395-409
[PubMed:17850253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leif Steil, Tamara Hoffmann, Ina Budde, Uwe Völker, Erhard Bremer
Genome-wide transcriptional profiling analysis of adaptation of Bacillus subtilis to high salinity.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(21);6358-70
[PubMed:14563871]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Mäder, H Antelmann, T Buder, M K Dahl, M Hecker, G Homuth
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: genome-wide analysis of the DegS-DegU regulon by transcriptomics and proteomics.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2002, 268(4);455-67
[PubMed:12471443]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Mukai, M Kawata-Mukai, T Tanaka
Stabilization of phosphorylated Bacillus subtilis DegU by DegR.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(24);7954-62
[PubMed:1459944]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M K Dahl, T Msadek, F Kunst, G Rapoport
Mutational analysis of the Bacillus subtilis DegU regulator and its phosphorylation by the DegS protein kinase.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(8);2539-47
[PubMed:1901568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, F Kunst, D Henner, A Klier, G Rapoport, R Dedonder
Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(2);824-34
[PubMed:1688843]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)