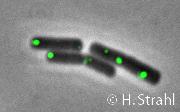
ClpX
- Description: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit (class III heat-shock protein)
| Gene name | clpX |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit |
| Function | protein degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: clpX | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ClpX | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 4.645 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1260 bp, 420 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | lonB, tig |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 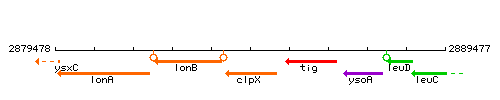
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
[hide]
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28220
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATPase/chaperone
- Protein family: clpX chaperone family (according to Swiss-Prot) ClpX (IP004487) InterPro, AAA+ -type ATPase (IPR013093) InterPro (PF07724) PFAM
Targets of ClpX-ClpP-dependent protein degradation
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasmic polar clusters, excluded from the nucleoid, induced clustering upon heat shock, colocalization with ClpP PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: homologue structure resolved 1UM8, structural model of B. subtilis ClpX available from hstrahl
- UniProt: P50866
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: clpX PubMed
- Additional information:
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: clpX::kan, clpX::spec and clpX::cat available from the Hamoen] Lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (both single copy and 2th copy in amyE locus, also as CFP and YFP variants) available from the Hamoen] Lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Aurelia Battesti, Susan Gottesman
Roles of adaptor proteins in regulation of bacterial proteolysis.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2013, 16(2);140-7
[PubMed:23375660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David W Adams, Jeff Errington
Bacterial cell division: assembly, maintenance and disassembly of the Z ring.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(9);642-53
[PubMed:19680248]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dorte Frees, Kirsi Savijoki, Pekka Varmanen, Hanne Ingmer
Clp ATPases and ClpP proteolytic complexes regulate vital biological processes in low GC, Gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(5);1285-95
[PubMed:17302811]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniel P Haeusser, Amy H Lee, Richard B Weart, Petra Anne Levin
ClpX inhibits FtsZ assembly in a manner that does not require its ATP hydrolysis-dependent chaperone activity.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(6);1986-91
[PubMed:19136590]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James Kain, Gina G He, Richard Losick
Polar localization and compartmentalization of ClpP proteases during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6749-57
[PubMed:18689476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Clp and Lon proteases occupy distinct subcellular positions in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6758-68
[PubMed:18689473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Stephan Zellmeier, Wolfgang Schumann, Thomas Wiegert
Involvement of Clp protease activity in modulating the Bacillus subtilissigmaw stress response.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 61(6);1569-82
[PubMed:16899079]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Richard B Weart, Shunji Nakano, Brooke E Lane, Peter Zuber, Petra Anne Levin
The ClpX chaperone modulates assembly of the tubulin-like protein FtsZ.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 57(1);238-49
[PubMed:15948963]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Janine Kirstein, Jörg Mostertz, Torsten Waldminghaus, Marcus Miethke, Holger Kock, Michael Hecker
Fine-tuning in regulation of Clp protein content in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(1);179-91
[PubMed:14679237]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hideaki Nanamiya, Emiko Shiomi, Mitsuo Ogura, Teruo Tanaka, Kei Asai, Fujio Kawamura
Involvement of ClpX protein in the post-transcriptional regulation of a competence specific transcription factor, ComK protein, of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biochem: 2003, 133(3);295-302
[PubMed:12761164]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tiina Pummi, Soile Leskelä, Eva Wahlström, Ulf Gerth, Harold Tjalsma, Michael Hecker, Matti Sarvas, Vesa P Kontinen
ClpXP protease regulates the signal peptide cleavage of secretory preproteins in Bacillus subtilis with a mechanism distinct from that of the Ecs ABC transporter.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(4);1010-8
[PubMed:11807061]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Serrano, S Hövel, C P Moran, A O Henriques, U Völker
Forespore-specific transcription of the lonB gene during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(10);2995-3003
[PubMed:11325926]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, E Witt, S Ohlmeier, R Hanschke, M Hecker
The clp proteases of Bacillus subtilis are directly involved in degradation of misfolded proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(11);3259-65
[PubMed:10809708]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, M Hecker
The first gene of the Bacillus subtilis clpC operon, ctsR, encodes a negative regulator of its own operon and other class III heat shock genes.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(24);6681-8
[PubMed:9852015]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Gerth, E Krüger, I Derré, T Msadek, M Hecker
Stress induction of the Bacillus subtilis clpP gene encoding a homologue of the proteolytic component of the Clp protease and the involvement of ClpP and ClpX in stress tolerance.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 28(4);787-802
[PubMed:9643546]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Gerth, A Wipat, C R Harwood, N Carter, P T Emmerson, M Hecker
Sequence and transcriptional analysis of clpX, a class-III heat-shock gene of Bacillus subtilis.
Gene: 1996, 181(1-2);77-83
[PubMed:8973311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)