Difference between revisions of "Sandbox"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' transcriptional antiterminator for | + | * '''Description:''' transcriptional antiterminator for ''[[sacB]]'' and ''[[sacX]]-[[sacY]]'' (acts at high sucrose concentrations) <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''sacY'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || ''ipa- | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || ''ipa-13r, sacS '' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of sucrose utilization | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of sucrose utilization | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 32 kDa, 5.883 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 840 bp, 280 aa |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[sacX]]'', ''[[gspA]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS: | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB15868]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image: | + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:sacY_context.gif]] |
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * '''Locus tag:''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU38420 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ | + | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/sacXY.html] |
| − | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+ | + | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+BG10559] |
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' binding to the mRNA of the ''[[ | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' binding to the mRNA of'' [[sacB]]'' and the ''[[sacX]]-[[sacY]]'' operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of sucrose) |
* '''Protein family:''' transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators | * '''Protein family:''' transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators | ||
| − | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[LicT]], [[ | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[LicT]], [[GlcT]], [[SacT]] |
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| − | * '''Interactions:''' [[PtsH]]-[[ | + | * '''Interactions:''' [[PtsH]]-[[SacY]] |
* '''Localization:''' | * '''Localization:''' | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1AUU 1AUU] (RNA-binding domain) |
| − | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ | + | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P15401 P15401] |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+ | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+BSU38420] |
* '''E.C. number:''' | * '''E.C. number:''' | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' | + | * '''Operon:''' ''[[sacX]]-[[sacY]]'' |
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] |
| − | * '''Regulation:''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' induction by sucrose (at high concentration) |
| − | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | + | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' induction by [[SacY]]-dependent RNA switch (transcriptional antitermination) |
| − | * '''Additional information:''' | + | * '''Additional information:''' |
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Stephane Aymerich |Stephane Aymerich]], Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France | ||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
| Line 118: | Line 120: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed> | + | <pubmed>2105292 8702561 11580842 1279678 9305643 9305644 10610766, </pubmed> |
| − | # | + | # Crutz AM, Steinmetz M, Aymerich S, Richter R, Le Coq D (1990) Induction of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis: an antitermination mechanism negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol 172:1043-1050. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2105292 PubMed] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Arnaud, M., Débarbouillé, M., Rapoport, G., Saier, M. H., and Reizer, J. (1996) In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of ''Bacillus subtilis''. J Biol Chem 271: 18966-18972. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8702561 PubMed] | # Arnaud, M., Débarbouillé, M., Rapoport, G., Saier, M. H., and Reizer, J. (1996) In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of ''Bacillus subtilis''. J Biol Chem 271: 18966-18972. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8702561 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Tortosa, P., Aymerich, S., Lindner, C., Saier, M.H., Jr., Reizer, J. and Le Coq, D. (1997) Multiple phosphorylation of SacY, a Bacillus subtilis antiterminator negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17230-17237. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9202047 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Tortosa, P., Declerck, N., Dutartre, H., Lindner, C., Deutscher, J., and Le Coq, D. (2001) Sites of positive and negative regulation in the Bacillus subtilis antiterminators LicT and SacY. Mol Microbiol 41: 1381-1393. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11580842 PubMed] | ||
# Aymerich, S. and Steinmetz, M. (1992) Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10410-10414. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1279678 PubMed] | # Aymerich, S. and Steinmetz, M. (1992) Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10410-10414. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1279678 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Manival, X., Yang, Y., Strub, M. P., Kochoyan, M., Steinmetz, M. and Aymerich, S. (1997) From genetic to structural characterization of a new class of RNA-binding domain within the SacY/BglG family of antiterminator proteins. EMBO J. 16, 5019-5029. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9305643 PubMed] | ||
| + | # van Tilbeurgh, H., Manival, X., Aymerich, S., Lhoste, J. M., Dumas, C. and Kochoyan, M. (1997) Crystal structure of a new RNA-binding domain from the antiterminator protein SacY of ''Bacillus subtilis''. EMBO J. 16, 5030-5036. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9305644 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Declerck, N., Vincent, F., Hoh, F., Aymerich, S. and van Tilbeurgh, H. (1999) RNA recognition by transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family: functional and structural comparison of the CAT domains from SacY and LicT. J. Mol. Biol. 294, 389-402. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10610766 PubMed] | ||
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 8 June 2009
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator for sacB and sacX-sacY (acts at high sucrose concentrations)
| Gene name | sacY |
| Synonyms | ipa-13r, sacS |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator |
| Function | regulation of sucrose utilization |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.883 |
| Gene length, protein length | 840 bp, 280 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sacX, gspA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 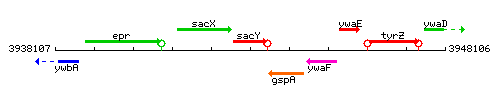
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38420
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binding to the mRNA of sacB and the sacX-sacY operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of sucrose)
- Protein family: transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 1AUU (RNA-binding domain)
- Swiss prot entry: P15401
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: induction by sucrose (at high concentration)
- Regulatory mechanism: induction by SacY-dependent RNA switch (transcriptional antitermination)
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Your additional remarks
References
P Tortosa, N Declerck, H Dutartre, C Lindner, J Deutscher, D Le Coq
Sites of positive and negative regulation in the Bacillus subtilis antiterminators LicT and SacY.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 41(6);1381-93
[PubMed:11580842]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Declerck, F Vincent, F Hoh, S Aymerich, H van Tilbeurgh
RNA recognition by transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family: functional and structural comparison of the CAT domain from SacY and LicT.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 294(2);389-402
[PubMed:10610766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H van Tilbeurgh, X Manival, S Aymerich, J M Lhoste, C Dumas, M Kochoyan
Crystal structure of a new RNA-binding domain from the antiterminator protein SacY of Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 1997, 16(16);5030-6
[PubMed:9305644]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Manival, Y Yang, M P Strub, M Kochoyan, M Steinmetz, S Aymerich
From genetic to structural characterization of a new class of RNA-binding domain within the SacY/BglG family of antiterminator proteins.
EMBO J: 1997, 16(16);5019-29
[PubMed:9305643]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Arnaud, M Débarbouillé, G Rapoport, M H Saier, J Reizer
In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 1996, 271(31);18966-72
[PubMed:8702561]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Aymerich, M Steinmetz
Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1992, 89(21);10410-4
[PubMed:1279678]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A M Crutz, M Steinmetz, S Aymerich, R Richter, D Le Coq
Induction of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis: an antitermination mechanism negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(2);1043-50
[PubMed:2105292]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Crutz AM, Steinmetz M, Aymerich S, Richter R, Le Coq D (1990) Induction of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis: an antitermination mechanism negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol 172:1043-1050. PubMed
- Arnaud, M., Débarbouillé, M., Rapoport, G., Saier, M. H., and Reizer, J. (1996) In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 271: 18966-18972. PubMed
- Tortosa, P., Aymerich, S., Lindner, C., Saier, M.H., Jr., Reizer, J. and Le Coq, D. (1997) Multiple phosphorylation of SacY, a Bacillus subtilis antiterminator negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17230-17237. PubMed
- Tortosa, P., Declerck, N., Dutartre, H., Lindner, C., Deutscher, J., and Le Coq, D. (2001) Sites of positive and negative regulation in the Bacillus subtilis antiterminators LicT and SacY. Mol Microbiol 41: 1381-1393. PubMed
- Aymerich, S. and Steinmetz, M. (1992) Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10410-10414. PubMed
- Manival, X., Yang, Y., Strub, M. P., Kochoyan, M., Steinmetz, M. and Aymerich, S. (1997) From genetic to structural characterization of a new class of RNA-binding domain within the SacY/BglG family of antiterminator proteins. EMBO J. 16, 5019-5029. PubMed
- van Tilbeurgh, H., Manival, X., Aymerich, S., Lhoste, J. M., Dumas, C. and Kochoyan, M. (1997) Crystal structure of a new RNA-binding domain from the antiterminator protein SacY of Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 16, 5030-5036. PubMed
- Declerck, N., Vincent, F., Hoh, F., Aymerich, S. and van Tilbeurgh, H. (1999) RNA recognition by transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family: functional and structural comparison of the CAT domains from SacY and LicT. J. Mol. Biol. 294, 389-402. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed