Difference between revisions of "SerA"
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 6336 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 6336 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 12316 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 12316 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9076 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4149 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 5497 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
** 1A614 ( ''serA''::''erm''), {{PubMed|3015878}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A614&Search=1A614 BGSC] | ** 1A614 ( ''serA''::''erm''), {{PubMed|3015878}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A614&Search=1A614 BGSC] | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 17 April 2014
- Description: phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
| Gene name | serA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase |
| Function | biosynthesis of serine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: serA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: serA | |
| MW, pI | 56 kDa, 5.617 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1575 bp, 525 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ypzE, aroC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 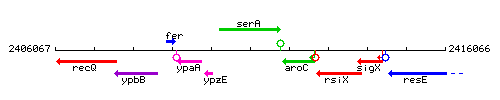
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed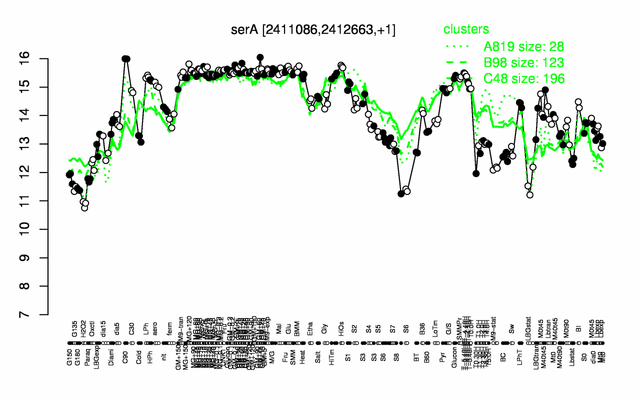
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, membrane proteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23070
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23070
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 3-phospho-D-glycerate + NAD+ = 3-phosphonooxypyruvate + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: D-isomer specific 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23070
- UniProt: P35136
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.95
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: serA PubMed
- Regulation:
- strongly repressed in response to glucose starvation in M9 medium PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 6336 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 12316 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9076 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4149 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 5497 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Imke G de Jong, Jan-Willem Veening, Oscar P Kuipers
Single cell analysis of gene expression patterns during carbon starvation in Bacillus subtilis reveals large phenotypic variation.
Environ Microbiol: 2012, 14(12);3110-21
[PubMed:23033921]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Bui Khanh Chi, Alexandra A Roberts, Tran Thi Thanh Huyen, Katrin Bäsell, Dörte Becher, Dirk Albrecht, Chris J Hamilton, Haike Antelmann
S-bacillithiolation protects conserved and essential proteins against hypochlorite stress in firmicutes bacteria.
Antioxid Redox Signal: 2013, 18(11);1273-95
[PubMed:22938038]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Bui Khanh Chi, Katrin Gronau, Ulrike Mäder, Bernd Hessling, Dörte Becher, Haike Antelmann
S-bacillithiolation protects against hypochlorite stress in Bacillus subtilis as revealed by transcriptomics and redox proteomics.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2011, 10(11);M111.009506
[PubMed:21749987]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dierk-Christoph Pöther, Dörte Becher, John D Helmann, Michael Hecker
S-cysteinylation is a general mechanism for thiol protection of Bacillus subtilis proteins after oxidative stress.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(36);25981-5
[PubMed:17611193]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
James R Thompson, Jessica K Bell, Judy Bratt, Gregory A Grant, Leonard J Banaszak
Vmax regulation through domain and subunit changes. The active form of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase.
Biochemistry: 2005, 44(15);5763-73
[PubMed:15823035]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V Azevedo, A Sorokin, S D Ehrlich, P Serror
The transcriptional organization of the Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome region between the spoVAF and serA genetic loci.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 10(2);397-405
[PubMed:7934830]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)