Difference between revisions of "RpoB"
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3434 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3434 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 10168 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 10168 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1411 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 800 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 802 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 17 April 2014
- Description: RNA polymerase beta subunit
| Gene name | rpoB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | RNA polymerase beta subunit |
| Function | transcription |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rpoB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RpoB | |
| MW, pI | 133 kDa, 4.731 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3579 bp, 1193 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ybxB, rpoC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 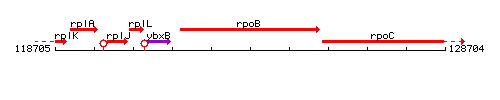
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed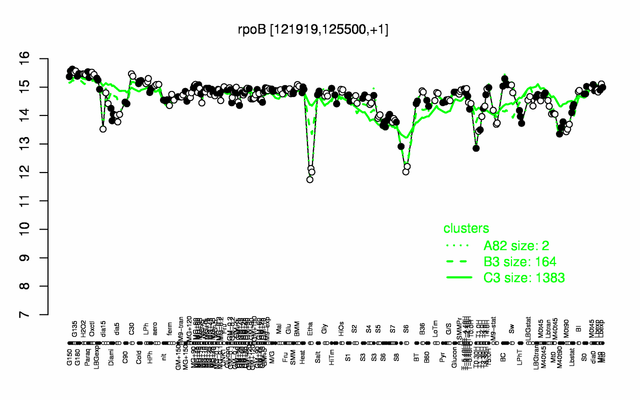
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription, essential genes, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01070
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01070
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
- mutations in mtrB, sigB, rpoB, and rpoC allow B. subtilis to grow with 4-fluorotryptophan rather than with tryptophan as a canonical amino acid of the genetic code PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Nucleoside triphosphate + RNA(n) = diphosphate + RNA(n+1) (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: RNA polymerase beta chain family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on (Arg-312 OR Arg-313), Arg-539, (Arg-693 OR Arg-694), Arg-827, and Arg-1106 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- RpoA-RpoB-RpoC PubMed, NusA-RpoB PubMed
- SigA-(RpoB-RpoC) PubMed, SigB-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigD-(RpoB-RpoC), SigE-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigF-(RpoB-RpoC), SigG-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigH-(RpoB-RpoC), SigI-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigK-(RpoB-RpoC), SigL-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigM-(RpoB-RpoC), SigV-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigW-(RpoB-RpoC), SigX-(RpoB-RpoC)
- SigY-(RpoB-RpoC), SigZ-(RpoB-RpoC)
- Xpf-(RpoB-RpoC), YlaC-(RpoB-RpoC)
- YvrI-RpoB PubMed,
- Mfd-RpoB PubMed
- Localization: membrane associated PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01070
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37870
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.7.6
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rpoB DBTBS
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3434 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 10168 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1411 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 800 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 802 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Lakshminarayan M Iyer, L Aravind
Insights from the architecture of the bacterial transcription apparatus.
J Struct Biol: 2012, 179(3);299-319
[PubMed:22210308]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Allen Chi-Shing Yu, Aldrin Kay-Yuen Yim, Wai-Kin Mat, Amy Hin-Yan Tong, Si Lok, Hong Xue, Stephen Kwok-Wing Tsui, J Tze-Fei Wong, Ting-Fung Chan
Mutations enabling displacement of tryptophan by 4-fluorotryptophan as a canonical amino acid of the genetic code.
Genome Biol Evol: 2014, 6(3);629-41
[PubMed:24572018]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ralf Moeller, Ignacija Vlašić, Günther Reitz, Wayne L Nicholson
Role of altered rpoB alleles in Bacillus subtilis sporulation and spore resistance to heat, hydrogen peroxide, formaldehyde, and glutaraldehyde.
Arch Microbiol: 2012, 194(9);759-67
[PubMed:22484477]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christopher T Brown, Laura K Fishwick, Binna M Chokshi, Marissa A Cuff, Jay M Jackson, Travis Oglesby, Alison T Rioux, Enrique Rodriguez, Gregory S Stupp, Austin H Trupp, James S Woollcombe-Clarke, Tracy N Wright, William J Zaragoza, Jennifer C Drew, Eric W Triplett, Wayne L Nicholson
Whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic analysis of Bacillus subtilis mutants following evolution under conditions of relaxed selection for sporulation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(19);6867-77
[PubMed:21821766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Takashi Inaoka, Kozo Ochi
Activation of dormant secondary metabolism neotrehalosadiamine synthesis by an RNA polymerase mutation in Bacillus subtilis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2011, 75(4);618-23
[PubMed:21512256]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shu Ishikawa, Taku Oshima, Ken Kurokawa, Yoko Kusuya, Naotake Ogasawara
RNA polymerase trafficking in Bacillus subtilis cells.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(21);5778-87
[PubMed:20817769]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lars F Westblade, Elizabeth A Campbell, Chirangini Pukhrambam, Julio C Padovan, Bryce E Nickels, Valerie Lamour, Seth A Darst
Structural basis for the bacterial transcription-repair coupling factor/RNA polymerase interaction.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(22);8357-69
[PubMed:20702425]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Xiao Yang, Seeseei Molimau, Geoff P Doherty, Elecia B Johnston, Jon Marles-Wright, Rosalba Rothnagel, Ben Hankamer, Richard J Lewis, Peter J Lewis
The structure of bacterial RNA polymerase in complex with the essential transcription elongation factor NusA.
EMBO Rep: 2009, 10(9);997-1002
[PubMed:19680289]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Amy E Perkins, Andrew C Schuerger, Wayne L Nicholson
Isolation of rpoB mutations causing rifampicin resistance in Bacillus subtilis spores exposed to simulated Martian surface conditions.
Astrobiology: 2008, 8(6);1159-67
[PubMed:19191541]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Amy E Perkins, Wayne L Nicholson
Uncovering new metabolic capabilities of Bacillus subtilis using phenotype profiling of rifampin-resistant rpoB mutants.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(3);807-14
[PubMed:17644585]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Claudia Rollenhagen, Haike Antelmann, Janine Kirstein, Olivier Delumeau, Michael Hecker, Michael D Yudkin
Binding of sigma(A) and sigma(B) to core RNA polymerase after environmental stress in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(1);35-40
[PubMed:12486038]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P J Lewis, S D Thaker, J Errington
Compartmentalization of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 2000, 19(4);710-8
[PubMed:10675340]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Yang, C W Price
Streptolydigin resistance can be conferred by alterations to either the beta or beta' subunits of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase.
J Biol Chem: 1995, 270(41);23930-3
[PubMed:7592585]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K J Boor, M L Duncan, C W Price
Genetic and transcriptional organization of the region encoding the beta subunit of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase.
J Biol Chem: 1995, 270(35);20329-36
[PubMed:7657605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)