Difference between revisions of "PrfB"
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 662 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 662 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1710 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1710 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 3037 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1746 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1959 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 17 April 2014
- Description: peptide chain release factor 2
| Gene name | prfB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | peptide chain release factor 2 |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: prfB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: PrfB | |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 4.85 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1099 bp, 366 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yvjA, secA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 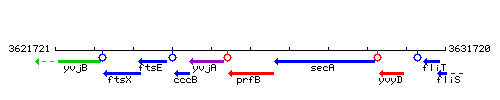
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35290
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35290
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binds to the ribosome through specific recognition of messenger RNA stop codons and triggers hydrolysis of the bond between the nascent polypeptide and the transfer RNA at the peptidyl-tRNA site, thereby releasing the newly synthesized protein. PrfB is highly specific for a U in the first stop-codon position and recognizes UAA and UGA
- Protein family: prokaryotic/mitochondrial release factor family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35290
- Structure:
- UniProt: P28367
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 662 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1710 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 3037 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1746 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1959 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Johan Sund, Martin Andér, Johan Aqvist
Principles of stop-codon reading on the ribosome.
Nature: 2010, 465(7300);947-50
[PubMed:20512119]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
M Herbort, M Klein, E H Manting, A J Driessen, R Freudl
Temporal expression of the Bacillus subtilis secA gene, encoding a central component of the preprotein translocase.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(2);493-500
[PubMed:9882663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)