Difference between revisions of "LysC"
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1459 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1459 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4406 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1282 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 806 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 17 April 2014
- Description: aspartokinase II (alpha and beta subunits)
| Gene name | lysC |
| Synonyms | ask, aecA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | aspartokinase II (alpha and beta subunits) |
| Function | biosynthesis of lysine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: lysC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: lysC | |
| MW, pI | 43 kDa, 4.643 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1224 bp, 408 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yslB, uvrC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 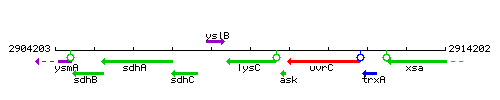
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed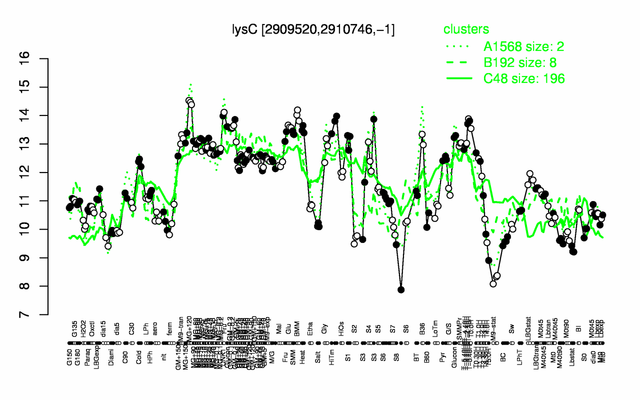
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU28470
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + L-aspartate = ADP + 4-phospho-L-aspartate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: aspartokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): DapG
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU28470
- Structure: 2RE1 (from Neisseria meningitidis mc58, 40% identity, 58% similarity)
- UniProt: P08495
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.4
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: lysC PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed, also degraded upon ammonium or amino acid starvation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1459 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4406 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1282 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 806 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Chien-Chi Lo, Carol A Bonner, Gary Xie, Mark D'Souza, Roy A Jensen
Cohesion group approach for evolutionary analysis of aspartokinase, an enzyme that feeds a branched network of many biochemical pathways.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(4);594-651
[PubMed:19946135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original Publications
The L-box riboswitch
Larry R Fiegland, Andrew D Garst, Robert T Batey, David J Nesbitt
Single-molecule studies of the lysine riboswitch reveal effector-dependent conformational dynamics of the aptamer domain.
Biochemistry: 2012, 51(45);9223-33
[PubMed:23067368]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sharnise N Wilson-Mitchell, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin
Analysis of lysine recognition and specificity of the Bacillus subtilis L box riboswitch.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2012, 40(12);5706-17
[PubMed:22416067]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Simon Blouin, Raja Chinnappan, Daniel A Lafontaine
Folding of the lysine riboswitch: importance of peripheral elements for transcriptional regulation.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(8);3373-87
[PubMed:21169337]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Trang Thi Phuong Phan, Wolfgang Schumann
Transcriptional analysis of the lysine-responsive and riboswitch-regulated lysC gene of Bacillus subtilis.
Curr Microbiol: 2009, 59(4);463-8
[PubMed:19636616]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Narasimhan Sudarsan, J Kenneth Wickiser, Shingo Nakamura, Margaret S Ebert, Ronald R Breaker
An mRNA structure in bacteria that controls gene expression by binding lysine.
Genes Dev: 2003, 17(21);2688-97
[PubMed:14597663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frank J Grundy, Susan C Lehman, Tina M Henkin
The L box regulon: lysine sensing by leader RNAs of bacterial lysine biosynthesis genes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2003, 100(21);12057-62
[PubMed:14523230]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Other original Publications
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Lu, T N Shevtchenko, H Paulus
Fine-structure mapping of cis-acting control sites in the lysC operon of Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1992, 71(1);23-7
[PubMed:1624109]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L M Graves, R L Switzer
Aspartokinase II from Bacillus subtilis is degraded in response to nutrient limitation.
J Biol Chem: 1990, 265(25);14947-55
[PubMed:2168395]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
N Y Chen, J J Zhang, H Paulus
Chromosomal location of the Bacillus subtilis aspartokinase II gene and nucleotide sequence of the adjacent genes homologous to uvrC and trx of Escherichia coli.
J Gen Microbiol: 1989, 135(11);2931-40
[PubMed:2559145]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Petricek, L Rutberg, L Hederstedt
The structural gene for aspartokinase II in Bacillus subtilis is closely linked to the sdh operon.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1989, 52(1-2);85-7
[PubMed:2557260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)