Difference between revisions of "IlvD"
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3104 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3104 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1545 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1545 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4271 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1398 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2083 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 17 April 2014
- Description: dihydroxy-acid dehydratase (2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate, 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate)
| Gene name | ilvD |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | dihydroxy-acid dehydratase (2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate, 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate) |
| Function | biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ilvD | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: ilvD | |
| MW, pI | 59 kDa, 5.315 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1674 bp, 558 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | brxA, ypgR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 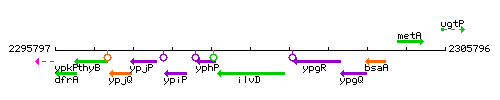
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
| Expression at a glance PubMed 500px | |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU21870
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU21870
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate = 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H2O (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU21870
- Structure:
- UniProt: P51785
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.2.1.9
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3104 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1545 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4271 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1398 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2083 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion: pGP522 (in pAC5), pGP235 (in pAC5), both available in Jörg Stülke's lab; a series of promoter deletions in pAC6 is available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Allison Kriel, Shaun R Brinsmade, Jessica L Tse, Ashley K Tehranchi, Alycia N Bittner, Abraham L Sonenshein, Jue D Wang
GTP dysregulation in Bacillus subtilis cells lacking (p)ppGpp results in phenotypic amino acid auxotrophy and failure to adapt to nutrient downshift and regulate biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(1);189-201
[PubMed:24163341]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of CodY-binding sites in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(4);1224-36
[PubMed:18083814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Susanne Hennig, Michael Hecker, Georg Homuth
Transcriptional organization and posttranscriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(8);2240-52
[PubMed:15060025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)