Difference between revisions of "DltA"
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1023 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1023 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2317 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2317 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1049 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 831 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 757 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:05, 17 April 2014
- Description: D-alanyl-D-alanine carrier protein ligase, alanylation of teichoic acid provides some resistance against positively charged antimicrobial peptides
| Gene name | dltA |
| Synonyms | ipa-5r, dae |
| Essential | no |
| Product | D-alanyl-D-alanine carrier protein ligase |
| Function | biosynthesis of teichoic acid |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: dltA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: DltA | |
| MW, pI | 55 kDa, 4.929 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1509 bp, 503 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywzH, dltB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 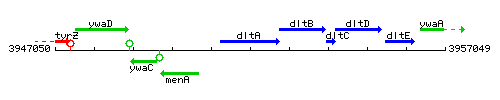
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigD regulon, SigM regulon, SigX regulon, Spo0A regulon, stringent response, YvrHb regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38500
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU38500
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + D-alanine + poly(ribitol phosphate) = AMP + diphosphate + O-D-alanyl-poly(ribitol phosphate) (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: DltA subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU38500
- Structure: 3E7X
- UniProt: P39581
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.1.1.13
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1023 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2317 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1049 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 831 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 757 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Mohamed Marahiel, Marburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Anthony W Kingston, Xiaojie Liao, John D Helmann
Contributions of the σ(W) , σ(M) and σ(X) regulons to the lantibiotic resistome of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 90(3);502-18
[PubMed:23980836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Veronica Guariglia-Oropeza, John D Helmann
Bacillus subtilis σ(V) confers lysozyme resistance by activation of two cell wall modification pathways, peptidoglycan O-acetylation and D-alanylation of teichoic acids.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6223-32
[PubMed:21926231]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Theresa D Ho, Jessica L Hastie, Peter J Intile, Craig D Ellermeier
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function σ factor σ(V) is induced by lysozyme and provides resistance to lysozyme.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6215-22
[PubMed:21856855]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Khan Tanjid Osman, Liqin Du, Yujiong He, Yu Luo
Crystal structure of Bacillus cereus D-alanyl carrier protein ligase (DltA) in complex with ATP.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 388(2);345-55
[PubMed:19324056]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Huma Yonus, Piotr Neumann, Stephan Zimmermann, Jürgen J May, Mohamed A Marahiel, Milton T Stubbs
Crystal structure of DltA. Implications for the reaction mechanism of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase adenylation domains.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(47);32484-91
[PubMed:18784082]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Masakuni Serizawa, Keisuke Kodama, Hiroki Yamamoto, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Junichi Sekiguchi
Functional analysis of the YvrGHb two-component system of Bacillus subtilis: identification of the regulated genes by DNA microarray and northern blot analyses.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2005, 69(11);2155-69
[PubMed:16306698]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Juergen J May, Robert Finking, Frank Wiegeshoff, Thomas T Weber, Nina Bandur, Ulrich Koert, Mohamed A Marahiel
Inhibition of the D-alanine:D-alanyl carrier protein ligase from Bacillus subtilis increases the bacterium's susceptibility to antibiotics that target the cell wall.
FEBS J: 2005, 272(12);2993-3003
[PubMed:15955059]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Min Cao, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic-function sigmaX factor regulates modification of the cell envelope and resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(4);1136-46
[PubMed:14762009]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, P Glaser, A Minutello, M A Strauch, K Leopold, W Fischer
Incorporation of D-alanine into lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Identification of genes and regulation.
J Biol Chem: 1995, 270(26);15598-606
[PubMed:7797557]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)