Difference between revisions of "AckA"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
| + | ** ** GP1902 (''ackA''::''aphA3'') (available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab) | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:09, 3 August 2015
- Description: acetate kinase
| Gene name | ackA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetate kinase |
| Function | overflow metabolism |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ackA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: ackA | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 5.191 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1185 bp, 395 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | moaB, ytxK |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 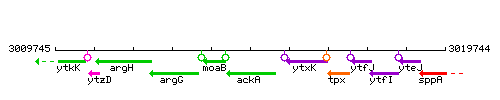
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed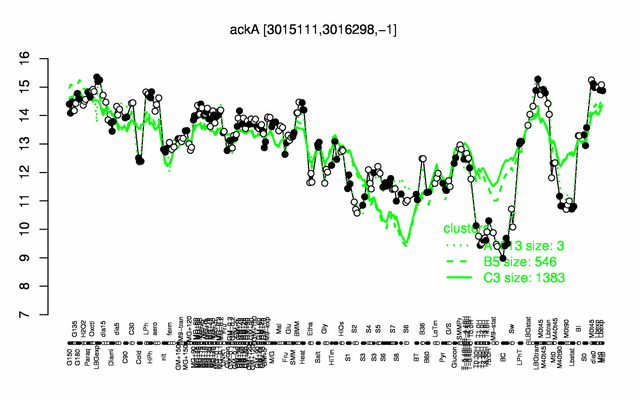
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ATP synthesis, carbon core metabolism, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29470
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: acetokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29470
- Structure: 2IIR (from Thermotoga maritima, 54% identity, 73% similarity)
- UniProt: P37877
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 3042 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1758 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2419 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- ** GP1902 (ackA::aphA3) (available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Maria A Schumacher, Mareen Sprehe, Maike Bartholomae, Wolfgang Hillen, Richard G Brennan
Structures of carbon catabolite protein A-(HPr-Ser46-P) bound to diverse catabolite response element sites reveal the basis for high-affinity binding to degenerate DNA operators.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(7);2931-42
[PubMed:21106498]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Robert P Shivers, Sean S Dineen, Abraham L Sonenshein
Positive regulation of Bacillus subtilis ackA by CodY and CcpA: establishing a potential hierarchy in carbon flow.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(3);811-22
[PubMed:16995897]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T R Moir-Blais, F J Grundy, T M Henkin
Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA promoter requires sequences upstream of the CcpA binding site.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(7);2389-93
[PubMed:11244084]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A J Turinsky, F J Grundy, J H Kim, G H Chambliss, T M Henkin
Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA gene requires sequences upstream of the promoter.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(22);5961-7
[PubMed:9811655]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, D A Waters, S H Allen, T M Henkin
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(22);7348-55
[PubMed:8226682]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)